1 MCU Market Overview
1.1 MCU Definition and Classification
A Microcontroller Unit (MCU) serves as a compact microcomputer chip, pairing a processor, memory, and input/output interfaces. At the heart lies the Central Processing Unit (CPU), executing program commands, while memory retains programs and data. The input/output interfaces facilitate communication with external devices.
Visualize an MCU as a small-scale computer, optimized for specific tasks, functioning within a single integrated circuit (IC) measuring just a few square centimeters. Its computational capacity may be modest, but its compact design, energy efficiency, and affordability position it as ideal for diverse uses that don't require extensive processing. From simple items like forehead thermometers and plastic toys to more complex systems like robotic arms and electric vehicles, the MCU serves as the command center.
Exhibit 1: MCU Internal Structure Diagram
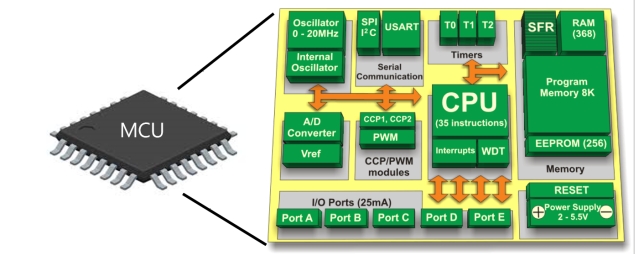
The MCU can be categorized into various types based on their applications and specific requirements.
·8-bit MCU: Mainly designed for low-power uses, such as controlling household appliances and gathering sensor data, these MCUs offer low processing power and limited memory. However, they stand out for their cost-effectiveness and user-friendly design.
·16-bit MCU: 16-bit MCUs deliver superior data processing and handle more complex computations than their 8-bit counterparts. They typically boast expanded memory and a variety of peripheral interfaces—ranging from communication options to timers and PWM channels—catering to diverse application demands. These MCUs fit nicely into moderately complex control roles, servicing industrial automation, premium home devices, and medical technologies. They balance cost with performance, meeting application requirements that need decent power, all while being budget-conscious.
·32-bit MCU: 32-bit MCUs shine with even greater processing power and enhanced memory capacity, making them perfect for intricate control systems and embedded tasks. They come equipped with robust computational abilities, extensive storage, and support for multiple peripherals, delivering high performance.
·MCU+FPGA: A hybrid approach merges MCU and FPGA technologies, optimizing data processing and control efficiency. This setup suits applications that necessitate high performance and unwavering reliability, particularly in sectors like industrial automation and aerospace.
1.2 Market Size and Growth Trend
The MCU market has steadily grown in recent years. From 2012 to 2021, the global market size consistently increased. Although the market dipped from 2019 to 2020 due to the pandemic's impact, it rebounded quickly to reach $19.6 billion in 2021. By 2022, the global MCU market expanded to $21.5 billion. In 2023, the market size stands at approximately $22.9 billion and is projected to hit $32 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 5.3%.
Exhibit 3: Global MCU Market Size Analysis from 2012 to 2022 (Unit: Billion USD)
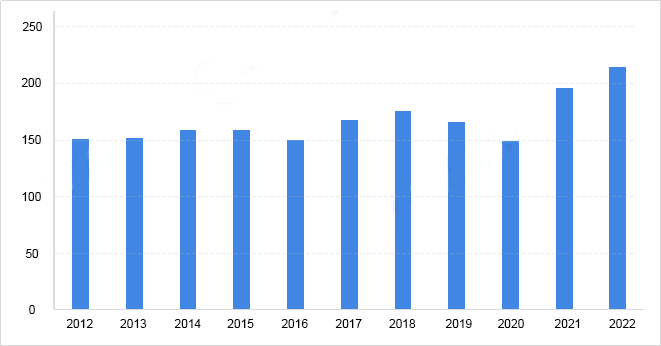
The growth trend for the MCU market shows strong promises, fueled by several pivotal factors. Key drivers include industry upgrades, particularly the rapid evolution of the IoT, rising adoption of automotive electronics, and surging demand for automation technology amid Industry 4.0. As IoT technologies advance, the appetite for 32-bit MCU chips is poised to rise sharply, especially within ADAS like automotive information systems and throttle control mechanisms. Innovations in production processes and enhancements in development environments will further advance the technology of 32-bit MCUs, where energy efficiency will become a primary competitive edge.
Although the global MCU market remains largely concentrated, with foreign manufacturers holding sway, domestic MCU suppliers show notable strength in the lower-tier market and significant potential for growth. As reported by IC Insights, worldwide microcontroller sales are anticipated to increase by 10%, with the global MCU market projected to hit $38 billion by 2028. The Chinese MCU market showcases particularly robust growth, with forecasts suggesting a steady compound annual growth rate of 7% from 2023 to 2026, aiming for a market size of 58.5 billion yuan by 2028.
1.3 MCU Price Trend
The 2024 analysis from a Chinese electronic information industry data engine highlights STMicroelectronics as a prominent MCU brand within the Top 20 popular models list. The key models include the TM32F103VET6 and STM32G473VET3. While both models belong to the STM32 series, they originate from distinct product lines with varying performance levels.
The STM32F103VET6 is an entry-level 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3 MCU, whereas the STM32G473VET3 represents a high-performance 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 MCU from STMicroelectronics. This distinction underscores a strategy of product differentiation based on technology and pricing. High-end products offer superior processing capabilities, enhanced integrated functions, and advanced technical features to cater to the rising demands of complex applications. Conversely, lower-end products continue to excel in cost-effectiveness and suitability for simpler applications.
